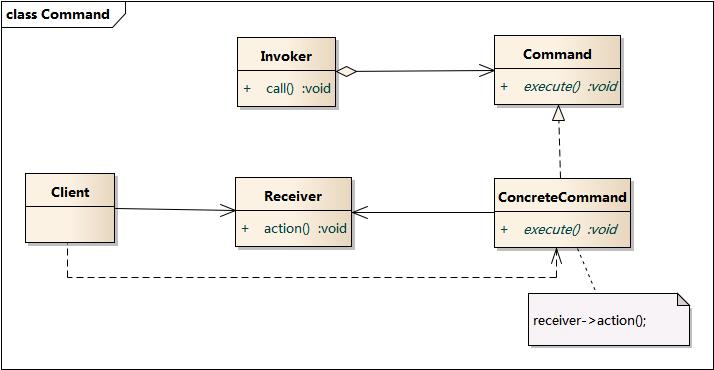
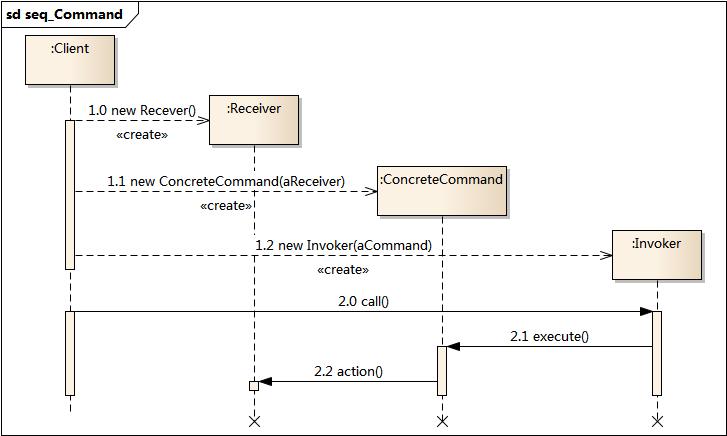
class Receiver {
constructor() {}
action1() {
console.log('我是客户要求的动作1 !');
}
action2() {
console.log('我是客户要求的动作2 !');
}
}
class Command {
constructor() {}
execute() {
console.log('必须重写该方法 !');
}
}
class ConcreteCommand extends Command {
constructor(receiver, action='') {
super();
this.receiver = receiver;
this.action = action;
}
execute() {
if (!this.receiver) {
return console.error('接受对象不能为空');
}
if (typeof this.receiver[this.action] !== 'function') {
return console.error('接收对象不存在该指令')
}
return this.receiver[this.action]();
}
}
class Invoke {
constructor() {
this.commandList = [];
}
add(command) {
if (command instanceof Command) {
this.commandList.push(command);
}
}
execute() {
for (let command of this.commandList) {
command.execute();
}
}
}
const receiver = new Receiver();
const invoke = new Invoke();
const command1 = new ConcreteCommand(receiver, 'action1');
const command2 = new ConcreteCommand(receiver, 'action2');
invoke.add(command1);
invoke.add(command2);
invoke.execute();